No products in the cart.
Open eCar
Open Source Software for Electric Vehicle (EV)
Open eCar project is open source software for electric car. The first release contains Electric Vehicle (EV) dashboard with a display of basic electric car parameters, such as speed, battery charging level and rate of power drainage in kW (kiloWatt).
Open eCar is written in C++ language with Qt5 stack and operates on Linux OS. It operates on Raspberry Pi 3 or Nvidia Jetson TX2, and any other hardware can be used as well.
I’m testing it on Mercedes Smart Fortwo Electric Vehicle. Open eCar project is open source software, so anyone is welcome to adaptate it to other electric cars models !
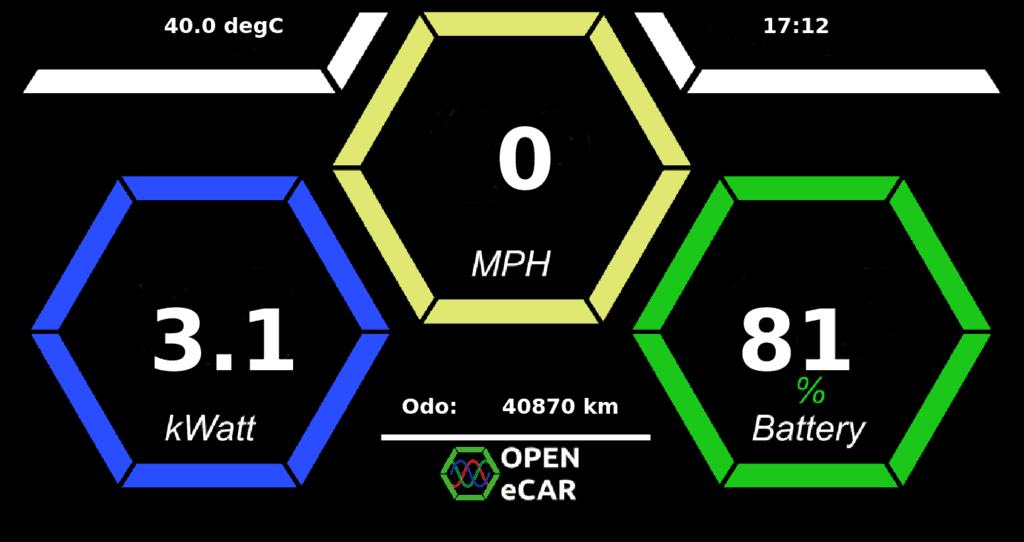
Open eCar dashboard while EV charging
Connection to electric car
Technically, we connect to electric car using an on-board diagnostics (OBD) port. The OBD port gives us an access to CAN bus, and we can get an access to all EV subsystems, such as battery management system (BMS), on board charger (OBC), coolant system, etc.
Special thanks to MyLab-odyssey and his amazing work on the CAN bus decode. Open eCar heavily rely on his findings.
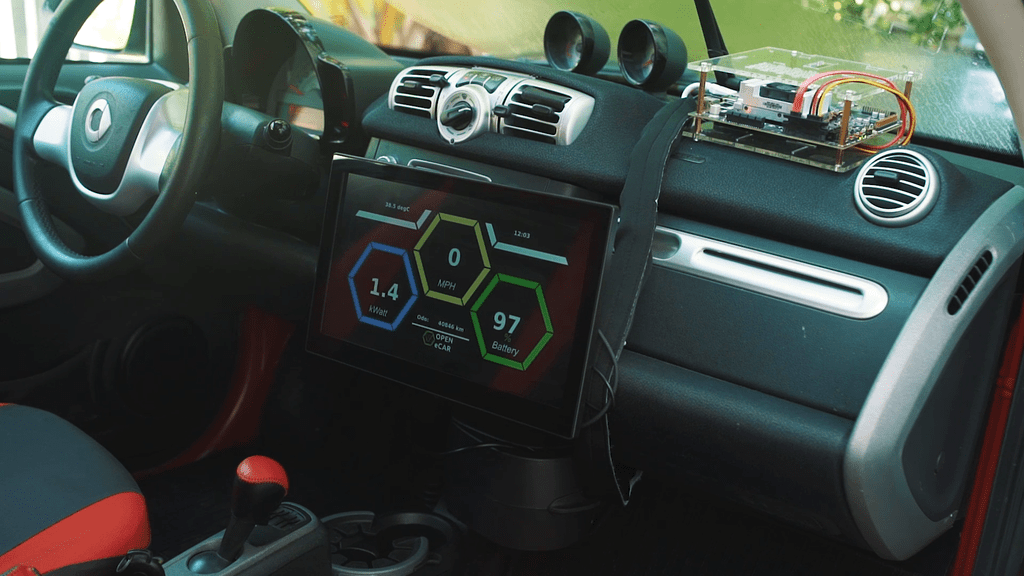 Open eCar and Nvidia Jetson TX2 installation inside Mercedes Smart Fortwo Electric
Open eCar and Nvidia Jetson TX2 installation inside Mercedes Smart Fortwo Electric
Source Сode and Сompilation
Fetch source code using following command:
git clone https://github.com/aospan/openecar_dashboard
then compile:
cd openecar_dashboard/desktop qmake . make
We should launch CAN bus daemon first:
slcand -o -c -s6 /dev/ttyACM0 can0 ifconfig can0 up
Now we are ready to launch Open eCar dashboard:
./openecar_dashboard -d can0
If everything is connected correctly, you should see a dashboard window with actual electric car data. For example, here is the screenshot of my Open eCar dashboard installed inside Smart Fortwo Electric EV:

Testing maximum acceleration. 62.1kW is currently draining from battery.
Mercedes Smart Fortwo Electric (2014) key specs
55 kW electric motor (74 horsepower, 130 Nm torque)
17.6kW lithium-ion battery (range of up to 145 km can be achieved)
Future Plans
- Debug window for Open eCar with more detailed information about battery status (can be used for battery life estimation), individual cell statistics, battery capacity measurements, main cooling loop info, high voltage contactor info, etc.
- In-vehicle infotainment (IVI) with audio and video entertainment, such as Video on demand, live TV and radio, music library, games, web access, etc.
- Off-grid (fully autonomous) EV charging from renewable sources (solar, wind, etc). Supercapacitors will be used as temporary energy storage in low light conditions when generation is not enough to conform of minimal J1772 requirements: 6 Amp * 110 Volt = 660 Watt or generation exceeds EV’s charging rate (3.3kW for Smart fortwo).
- Backup power for house. EV can act as a power source in case of power outages. This is so called vehicle-to-grid technology.
- Power source for utility needs. EV can power tools on construction sites. Provide illumination with bright LEDs, etc.
- Edge computing (“data center on wheels”, IoT, smart city). Electric vehicles can be used not only as transport platforms, but as powerful computing ones on the wheels.
- Such EVs can be used as ground stations for upcoming satellite Internet – Oneweb and SpaceX constellations with LEO satellites. Such ground systems can augment satellite connectivity with local computing and caching (CDN, etc.) and peer-to-peer mesh network. And it can work as 4G/5G cell tower or WiFi access point as well.
- Autonomous driving (driverless car). EVs can be used not only for passenger moving, but also for all above mentioned utility needs – off-grid charging, edge computing, mesh network, satellite connectivity, 4G/5G network, smart city and many more.